We all know the importance of batteries in our daily lives. From powering our smartphones to running electric cars, batteries have become an indispensable part of modern technology. Among the different types of batteries available, lithium-ion batteries are rapidly gaining popularity due to their high energy density, long life span, and low maintenance cost.
In this ultimate guide, we will explore everything you need to know about lithium-ion batteries. We’ll cover topics like how they work, their advantages and disadvantages, applications, and safety measures.
What is a Lithium Ion Battery?
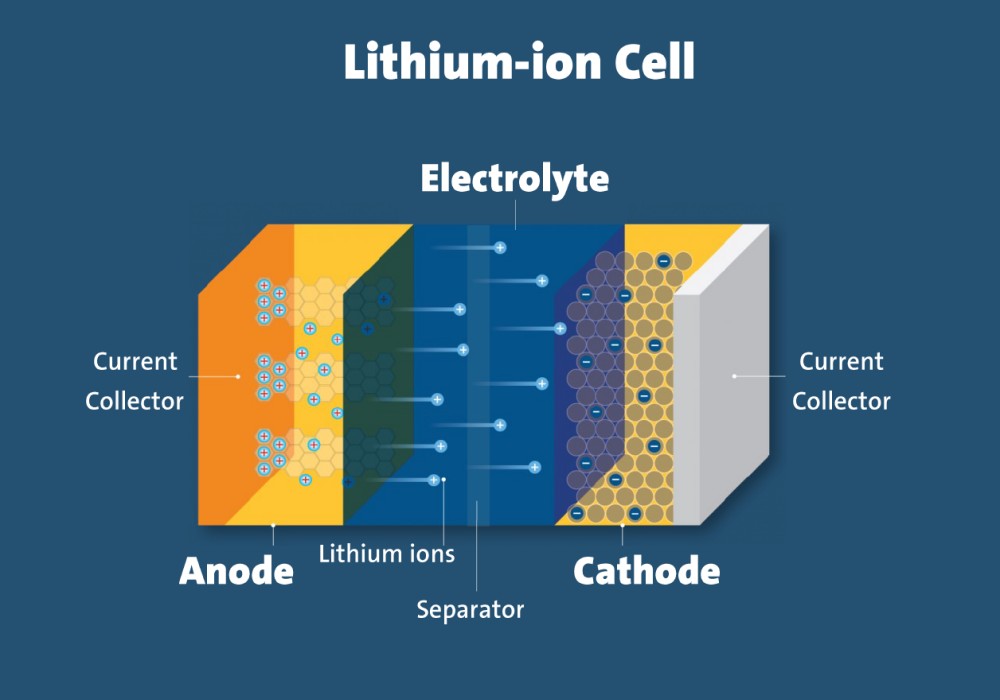
A lithium-ion battery is a rechargeable battery that uses lithium ions as the primary material for its electrodes. The battery consists of two electrodes – the cathode and the anode – separated by an electrolyte. When the battery is charged, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte. During discharge, the process reverses, and the lithium ions move back to the cathode, generating electrical energy.
Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries
High Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries have a higher energy density compared to other rechargeable batteries. This means that they can store more energy per unit volume or weight, making them ideal for portable devices like laptops and smartphones.
Long Life Span: Lithium-ion batteries have a longer life span than other rechargeable batteries. They can be recharged hundreds of times without significant capacity loss. This makes them a cost-effective option in the long run.
Low Maintenance: Lithium-ion batteries require very little maintenance compared to other rechargeable batteries. They don’t need any priming or cycling, and there’s no memory effect. This makes them easy to use and maintain.
Quick Charging: Lithium-ion batteries can be charged quickly compared to other rechargeable batteries. They can be charged up to 80% in just an hour, making them a convenient option for people on the go.
Disadvantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries
High Cost: Lithium-ion batteries are more expensive than other rechargeable batteries. This is due to the high cost of materials and manufacturing processes involved in their production.
Sensitivity to High Temperatures: Lithium-ion batteries can be sensitive to high temperatures. Exposure to high temperatures can cause the battery to degrade quickly, reducing its overall life span.
Safety Concerns: Lithium-ion batteries can be a safety hazard if not handled properly. They can catch fire or explode if overcharged, damaged, or exposed to extreme conditions.
Applications of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have a wide range of applications, from powering small devices like smartphones and laptops to large-scale applications like electric vehicles and energy storage systems. Here are some of the most common applications of lithium-ion batteries:
Consumer Electronics: Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in consumer electronics like smartphones, laptops, tablets, and smartwatches.
Electric Vehicles: Lithium-ion batteries are rapidly gaining popularity as the primary power source for electric vehicles. They offer a high energy density, quick charging, and long life span, making them an ideal choice for electric cars.
Aerospace: Lithium-ion batteries are used in aerospace applications like satellites, space probes, and rovers. They provide a reliable and efficient power source for these critical missions.
Energy Storage Systems: Lithium-ion batteries are also used in energy storage systems like solar power banks and home energy storage systems. They enable homeowners to store excess solar energy generated during the day and use it during peak hours.
Safety Measures for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries can be safe if handled properly. Here are some safety measures you should follow when using lithium-ion batteries:
Avoid Overcharging: Overcharging can cause the battery to degrade quickly and reduce its overall life span. Always use the charger provided with the battery and avoid charging it for extended periods.
Keep Away from Heat Sources: Exposure to high temperatures can cause the battery to catch fire or explode. Avoid leaving the battery in direct sunlight or near heat sources like radiators and stoves.
Use a Protective Case: Always use a protective case when carrying lithium-ion batteries. This will prevent them from coming into contact with other metallic objects that can cause a short circuit.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion batteries are becoming increasingly popular due to their high energy density, long life span, and low maintenance cost. They have a wide range of applications, from powering small devices like smartphones and laptops to large-scale applications like electric vehicles and energy storage systems. However, they can be a safety hazard if not handled properly. By following the safety measures outlined in this guide, you can safely u
